What is Blockchain?
It's a blockchain of databases (Blockchain), where the storage media is not linked together by a single server. The databases store information electronically (digitally). The innovation of blockchain is that it guarantees the security and accuracy of data recording and provides trust without the need for a third party.
Blockchain is an information recording system that makes it impossible to cheat, alter or hack and is a Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) where transactions are recorded with an immutable cryptographic signature called a hash.
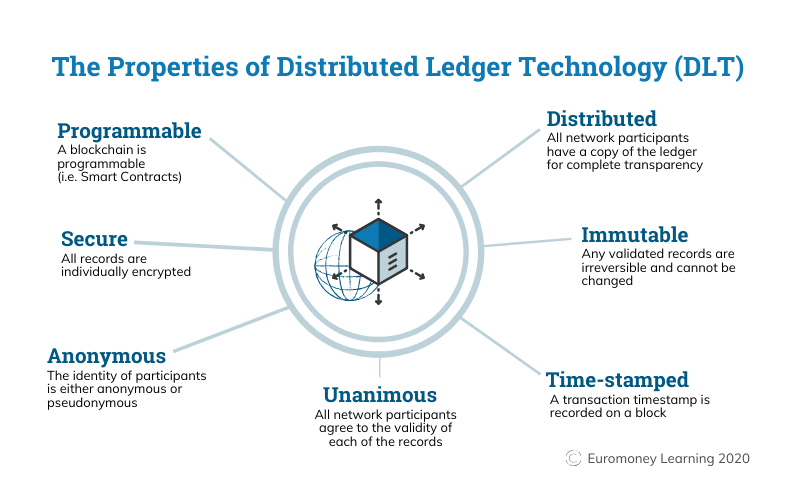
Features of DLT Technology:
- Programmable - DLT is programmable;
- Secure - all records are encrypted;
- Distributed - DLT is distributed, i.e. there is a copy of the ledger for full transparency;
- Immutable - checked records are irreversible and cannot be changed;
- Time-Stamped - the time of the transaction is recorded in a block;
- Anonymous - the identity of the participants is not disclosed;
- Unanimous - network participants agree on the validity of each entry.
The active use of blockchain is associated with cryptocurrencies (virtual currencies). Virtual currency is a digital expression of value that functions as (1) a store of value; and/or (2) a unit of account; and/or (3) a medium of exchange, but has no legal payment status in any jurisdiction.
Virtual currency must be distinguished from fiat currencies (aka "real money" or "national currencies"), Fiat money circulates, is accepted and used as a means of payment in the country that issues it.
Blockchains have evolved successfully in recent years depending on the assembly and configuration. The content contained in the blocks, as well as the actions of network participants, can be controlled depending on how the blockchain is configured and what business goal will be pursued.
The most common are public and private blockchains, which are used in private companies and cryptocurrency networks. A third type is authorized blockchains, which are also gaining popularity.
What is a private blockchain?
It is a system where permission is required, with access controls and restrictions on the people who participate in the network. One or more entities can control the network, resulting in dependence on third parties for transactions.
In this type of blockchain, only the people who participate in the transaction know about the transaction. Hyperledger Fabric is an example of a private blockchain. It is an industry-ready platform with DLT, permissioned networks, and open source.
What is public blockchain?
A public blockchain is publicly available and requires no permission. Anyone can join it online to read, learn or participate. It's decentralized and has no entity that controls it. The data in the public blockchain is secured, as it cannot be changed, due to the fact that the inclusion of a transaction in the blockchain is a validation and is an irreversible process under the rules of distributed ledger technology.
Public blockchain has the computing power needed to maintain a distributed ledger on a large scale. It is worth noting that to achieve consensus, each node in the network must solve a resource-intensive, complex problem to keep all nodes in sync. Consensus (consensus algorithm) is a way for all nodes (computers) of a decentralized network to reach agreement between the generated blocks, or, more simply, for all computers to agree on adding each new block to the network.
|
Transaction |
Transaction |
Transaction |
|
Public key of the first owner |
Public key of the second owner |
Public key of the third owner |
|
Hash |
Hash |
Hash |
|
Digital signature of the zero owner |
Digital signature of the first owner |
Digital signature of the second owner |
|
Private key of the first owner |
Private key of the second owner |
Private key of the third owner |
The difference between private and public blockchain
The main difference lies in the level of access that is granted to participants. To maximize decentralization, public blockchains are completely open. Anyone can participate by adding or validating data.
The most common examples of public blockchain are Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH). Both of these cryptocurrencies are created using open source code, which can also be viewed and used by anyone.
- Blockchain accessibility
Public blockchain is all about accessibility and this can be seen in the way it is used.
In private blockchains, only one participant or nodes authorized by that single administrator have the right to record information. These are centralized, personalized systems because there is a hierarchy of authority. Participants are given full or limited access at the discretion of the network.
As a result, a private blockchain is more centralized because only a small group controls the network. The most common examples of private blockchains are Ripple (XRP) and Hyperledger.
- Anonymity of blockchain users
Some public blockchains also allow anonymity, while private blockchains don't. For example, anyone can buy and sell bitcoins without revealing their identity. This allows everyone to be treated equally. In a private blockchain, on the other hand, everyone's identity is known. This is usually because private blockchain is used in corporate and business environments where it is important to know who the participants are.
- Public and Private Blockchain Comparison
|
Basis for comparison |
Public |
Private |
Note |
|
1. Access |
Any participant can read, write and participate, hence an unrestricted blockchain |
Reading and writing are done by invitation, hence it's a permissioned blockchain. |
Public blockchain is commonly available, and that is its main advantage |
|
2. Network Actors |
Don't know each other |
Must know each other |
Public blockchain respects the anonymity of participants, there is no need to disclose their personal data |
3. Decentralized vs Centralized |
Centralized |
Decentralized |
More centralized, as a small group controls the network |
4. Speed |
Slow |
Rapid |
In a private blockchain network, there are fewer participants, and it takes less time to reach consensus. |
|
5. Transactions pre second |
Transactions per second are less than in a private blockchain |
More transactions per second than in public blockchain |
Public blockchains process seven transactions per second. A private blockchain can perform thousands of transactions per second. |
|
6. Security |
A public network is more secure due to decentralization and active participation. Because of the greater number of nodes in the network, it is almost impossible for "attackers" to attack the system and gain control of the consensus network |
Private blockchain is more vulnerable to hacks, risks, and data leakage/manipulation. |
Attackers can easily compromise the entire private blockchain network. Consequently, it is less secure. |
|
7. Energy Consumption |
It consumes more power than a private blockchain. |
It consumes much less energy and power. |
A public blockchain requires a significant amount of energy to function. |
|
8. Consensus Algorithms |
Some of them are proof of work, proof of stake, proof of space, etc. |
Proof of Elapsed Time, Raft and Istanbul BFT can only be used for private blockchains |
For a private blockchain, it makes no sense to use proof-of-work or proof-of-stake; information enters the blocks without delay and requires no additional confirmation, thereby increasing the speed of transactions. |
|
9. Attacks |
In a public blockchain, no one knows for sure the identity of each validator (a node in the blockchain system that performs the tasks of keeping the network up and running). |
There is no chance of a minor collision in a private blockchain, so every validator is known. |
For a public blockchain, the risk of a potential collision or attack increases by 51% (a group of miners who control more than 50% of the network's computing power). |
|
10. Effects |
The potential to disrupt existing business models by eliminating intermediaries. The cost of creating and launching decentralized apps is reduced. |
Reduces transaction costs and data redundancy, replaces legacy systems, and simplifies document processing. |
There is no need for a public blockchain to maintain servers, system administrators, and therefore the cost of infrastructure is lower than in a private blockchain. |
|
11. Examples |
Bitcoin, Ethereum, Monero, Zcash, Dash, Litecoin, Stellar, Steemit. |
R3 (banks), EWF (energy), B3i (insurance), Corda |
The advantages of public and private blockchain
Most people see blockchain as a way to build trust and security, which makes public blockchain much more attractive. However, it is held back by speed and scalability. Public blockchain is popular among projects that serve large communities because of the transparency, which in turn fosters greater trust.
Importantly, there have been concerns about the privacy of public blockchain. Some believe that sensitive data should not be stored in a public blockchain. Even if information is encrypted, it is forever public and there is a chance that the encryption could be compromised at some point.
Who would benefit from private blockchain
The corporate world and financial institutions may be better off with a private blockchain if they are going to store information in it. In this case, companies need to know the composition of the network participants and their type of access.
Blockchain technology is constantly evolving and, in particular, public blockchain has undergone significant changes over the past few years. As things continue to evolve, the current shortcomings of public blockchains may become a thing of the past.
Hybrid blockchain
There are many opportunities to develop both private and public blockchain, and each has its own uses. Creating a hybrid solution could also be a viable solution for businesses.
Some projects are working on a model that combines a decentralized structure with centralized elements. The best of both worlds is Security and Transparency, along with Scalability and Efficiency.
Closing remarks
Blockchain is based on the idea of granting Freedom and Self-Sufficiency to humanity. The concept of regulating modern innovation, including blockchain, is impossible without the principle of "Technology Neutrality".
NB! Directive 2002/212 of the European Parliament sets out the principle of "Technological neutrality" as follows: "neither imposes nor discriminates in favour of the use of a particular type of technology"
That is, it is important to support efforts to digitize areas of life, but to be neutral about which technology is best suited to achieve a particular goal.
The focus of regulation in innovation should always be the creation of technical standards for its regulation, as well as ethical principles and principles of good governance.
Consequently, international organizations, governments, and state authorities of various countries have no right to prohibit, restrict, or even more so to declare criminal the technology of Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies based on it.
And in general, it doesn't matter what kind of blockchain you need, speed of transactions or maximum security of assets. That's the reason you're better off with Broex (https://broex.io/ ) for buying and storing cryptocurrencies, which has the following advantages:
- quick registration (identification) on the website;
- convenient mobile app;
- 24/7 support;
- easy deposit;
- low fees;
- the opportunity to buy and store 40 cryptocurrencies on Broex website is available to every client.
