Storj is based on blockchain technology and uses peer-to-peer protocols to provide decentralized, secure, private, and encrypted cloud storage.
Storj DCS (decentralized cloud storage) automatically encrypts all files before being uploaded, so your data is only in your hands and in the hands of those you share it with.
Once encrypted, each object is divided into parts that are indistinguishable from parts of any other object, which also ensures that your data is always available.
The parts of the object are stored individually in a global network of storage nodes. The object is never held in one place; outages, downtime, and data leaks become a thing of the past.
When you retrieve an object, only 29 of its 80 parts are required to recover it. With no single point of failure, your data is available quickly around the world at all times.
The Storj Network (STORJ) aims to provide secure, cost-effective distributed cloud storage that returns ownership of data to users. Unlike centralized cloud storage, a distributed architecture with end-to-end encryption of every file protects against attacks, improves reliability, increases upload/download speeds and boosts capacity.
Storj Labs runs Tardigrade, a developer tool that claims to outperform or be on par with all other major cloud providers (S3, Google, Microsoft) in durability, performance and security.
Storj Labs runs Tardigrade, a developer tool that claims to outperform or be on par with all other major cloud providers (S3, Google, Microsoft) in durability, performance and security.
Users can also receive a rent for additional disk space. Files are broken down into smaller components and distributed across many devices, with users retaining control over their keys, giving them access to the files at any time. As a result, this decentralized cloud storage model creates additional security for users compared to centralized cloud storage providers.
Team

Storj was founded by Sean Wilkinson in May 2014. Wilkinson was a software developer in Atlanta. He realized how blockchain technology could be used to create a decentralized cloud storage network.
Together with his co-founder John Quinn, the first white paper was published in late 2014. Since then, the concept and details have changed. The current version of Storj, V3, was launched in the middle of 2019.
In addition to being a blockchain enthusiast, Quinn had an extensive background in business development. Before launching his own projects (including Storj), he worked in investment banking. In May 2015, the concept was finalized in the form of a company, Storj Labs Inc.
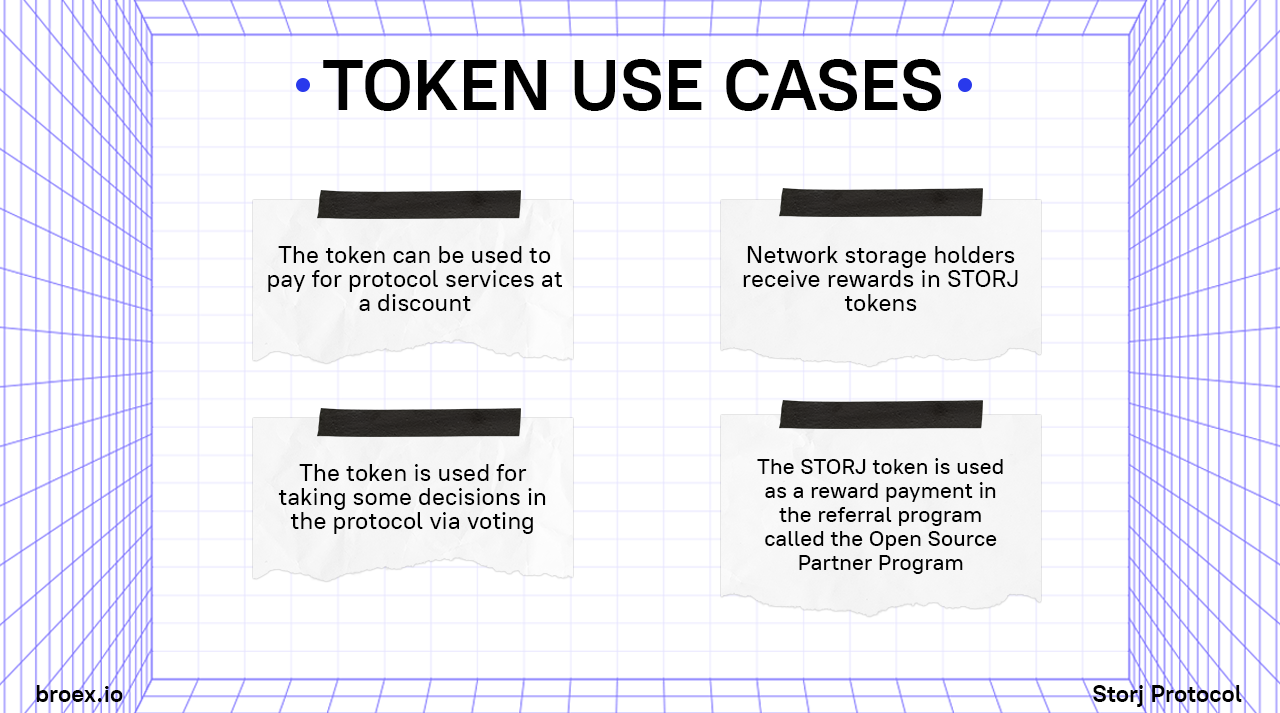
Application of STORJ
Tokenomics
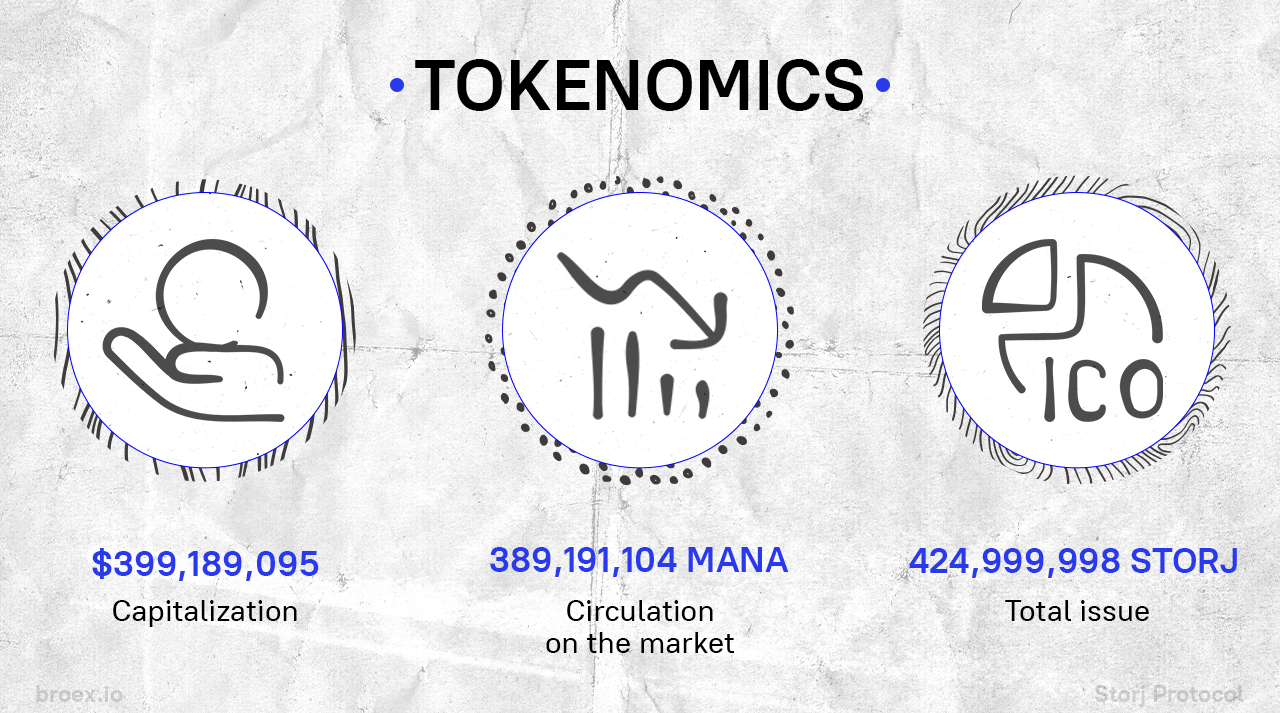
In 2014, the platform was able to raise 910 BTC (worth about $460,000) in a public crowdsale. Three years later, it raised $3 million in an initial funding round and then held a token sale, raising around $30 million more that year.
Before the STORJ token was released, there was a legacy SJCX token with 500 million in stock, of which 50 million was distributed, and the other 450 million was kept by Storj Labs.
In 2017, a total of 500 million STORJ tokens were issued, and the legacy SJCX token was discontinued, along with the transition from the Bitcoin to Ethereum blockchain. A total of 72 million STORJs were distributed to the public in the pre and main sale, raising $30 million for the project. Another 20.66 million SJCX remained in circulation and could be converted to STORJ at a 1:1 rate until December 2017. During that time, the 450 million SJCX tokens held by Storj were converted into 450 million STORJ tokens.
After these distributions, Storj retained 375 million, with 75 million being burned, leaving the project with 300 million tokens. 245 million of these remain locked up until June 20, 2018, as they were originally scheduled to be issued on December 20, 2017. The remaining 55 million tokens are unlocked and available for use by Storj to pay vendors, including farmers.
The burning of 75 million tokens brings the total number of tokens to 425 million.
Risks

Growth Prospects
The project is 119th in the overall CMC ranking and 13th in the Web3 ranking
In addition to being open source, our new V3 network also provides financial support to open source companies, allowing them to generate revenue every time their users store data in the cloud.
Many platforms fail to tackle these design limitations adequately, resulting in decentralized cloud storage networks with unreasonable latency, low file longevity, high cost and poor performance.
By addressing these issues, Storj V3 provides a network that outperforms centralized cloud storage platforms in many ways.
As a decentralized cloud storage network, Storj has something more to offer than that. Unlike traditional cloud storage, which stores data in huge data centers, Storj runs on a network of thousands of independent computers.
Anyone with a few extra terabytes of space can become a node in the platform by installing Tardigrade. All that's required is a reliable and stable Internet connection.
Network efficiency means that hosts pay much less to store their data than with traditional cloud storage services.
Earlier this year, we took a look at the Web3 landscape and were concerned that most of the NFT miners had no idea that their NFTs might disappear.
The most common misconception I've heard is that miners think that NFTs are stored on the blockchain. However, in reality, only links to NFTs are stored on the blockchain, and the NFTs themselves just lie on the Internet. They either use traditional Web 2.0 methods to host content or move to the more decentralized Web3 model.
While the creation of NFTs is in full swing, IPFS providers are using centralized providers like Amazon S3 to store data. Our view is that we can do better with our storage service.
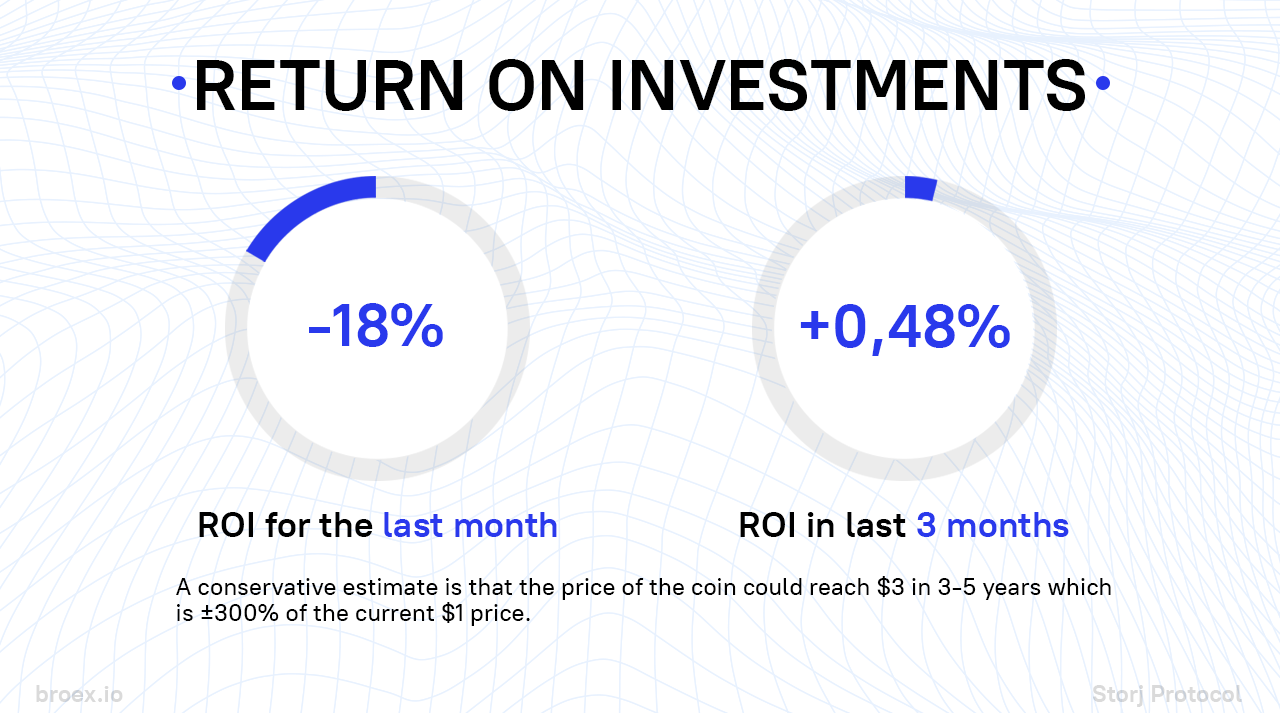
Optimistic forecast $7.
Realistic forecast $3.
Pessimistic forecast $2.